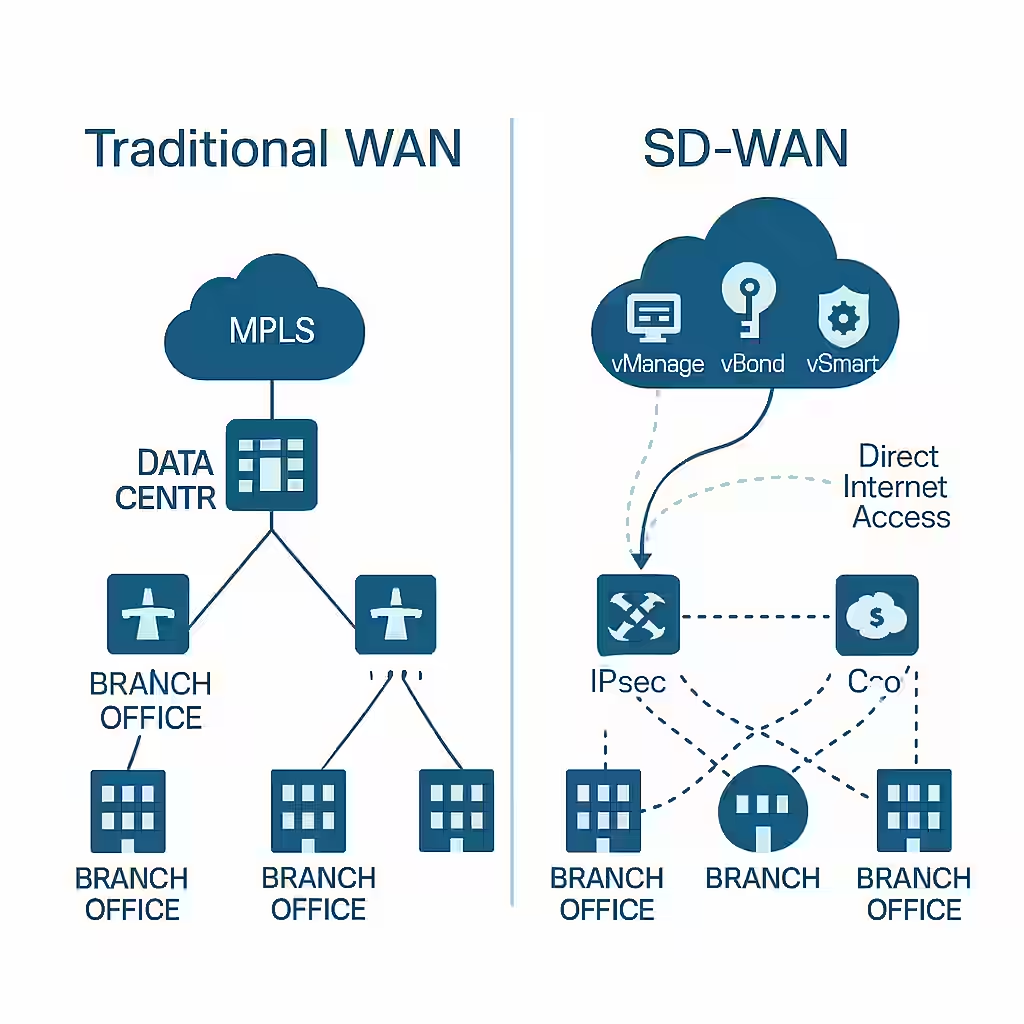
The way enterprises connect remote branches to their data centers and applications has dramatically changed. Traditional WANs served well in the era of centralized computing, but as cloud adoption surged, so did the need for a more agile, scalable, and cost-effective solution—enter SD-WAN.
The WAN Evolution
Traditional WANs relied heavily on private circuits like MPLS for site-to-site connectivity. These networks were dependable but expensive, with limited flexibility. Modern businesses now need dynamic access to cloud applications, SaaS platforms, and hybrid environments—all with predictable performance and security.
Key Concepts
Traditional WAN
- Architecture: Hub-and-spoke, where branch offices connect to a central data center via MPLS.
- Routing: Static or manually configured routing policies.
- Traffic Flow: All branch internet traffic is typically backhauled to the data center.
- Management: Device-by-device configuration, often requiring on-site IT support.
- Security: Centralized at the data center, with firewalls and security stacks.
Limitations:
- Costly MPLS circuits
- Poor cloud performance due to backhaul
- Limited visibility and control
- Complex provisioning and scaling
Software-Defined WAN (SD-WAN)
- Architecture: Cloud-first, with direct-to-internet and inter-branch IPsec tunnels.
- Routing: Centralized policy-driven routing via controllers like Cisco vSmart.
- Traffic Flow: Internet-bound traffic can exit directly from the branch (DIA).
- Management: Centralized via GUI dashboards (e.g., Cisco vManage).
- Security: Integrated or cloud-based, with encryption, firewall, and segmentation.
Advantages:
- Cost savings through broadband and LTE use
- Improved cloud access and application performance
- Simplified provisioning with zero-touch deployment
- Granular control with application-aware policies
Side-by-Side Comparison
| Feature | Traditional WAN | SD-WAN |
|---|---|---|
| Transport | Primarily MPLS | MPLS, Broadband, LTE |
| Architecture | Hub-and-Spoke | Cloud-Optimized, Any-to-Any |
| Security | Centralized | Distributed and Integrated |
| Traffic Handling | Backhauled | Direct Internet Access (DIA) |
| Provisioning | Manual, Complex | Zero-Touch Provisioning (ZTP) |
| Policy Control | Static | Centralized and Dynamic |
| Cloud Integration | Limited | Native and Optimized |
Considerations for Migration
- Business Goals: Cost reduction, cloud readiness, remote work?
- Network Size: Number of branches, cloud dependencies.
- Security Needs: Compliance, segmentation, threat protection.
- IT Skillset: Comfort with centralized management and automation.
Config Insight: SD-WAN Tunnel Verification
show sdwan control connectionsThis command checks the control plane tunnel status on a Cisco SD-WAN edge device.