Wireless networks are no longer optional—they’re essential. But not all wireless setups are created equal. Depending on the size, location, and goals of a business, the right deployment model can drastically improve performance, manageability, and scalability. Understanding the strengths and use cases of different wireless deployment models is key to designing a robust network.
Why Wireless Deployment Models Matter
Selecting the wrong wireless architecture can lead to poor coverage, scalability issues, and difficult management. A proper model ensures better performance, centralized control, and optimized costs based on the organization’s needs.
Key Concepts
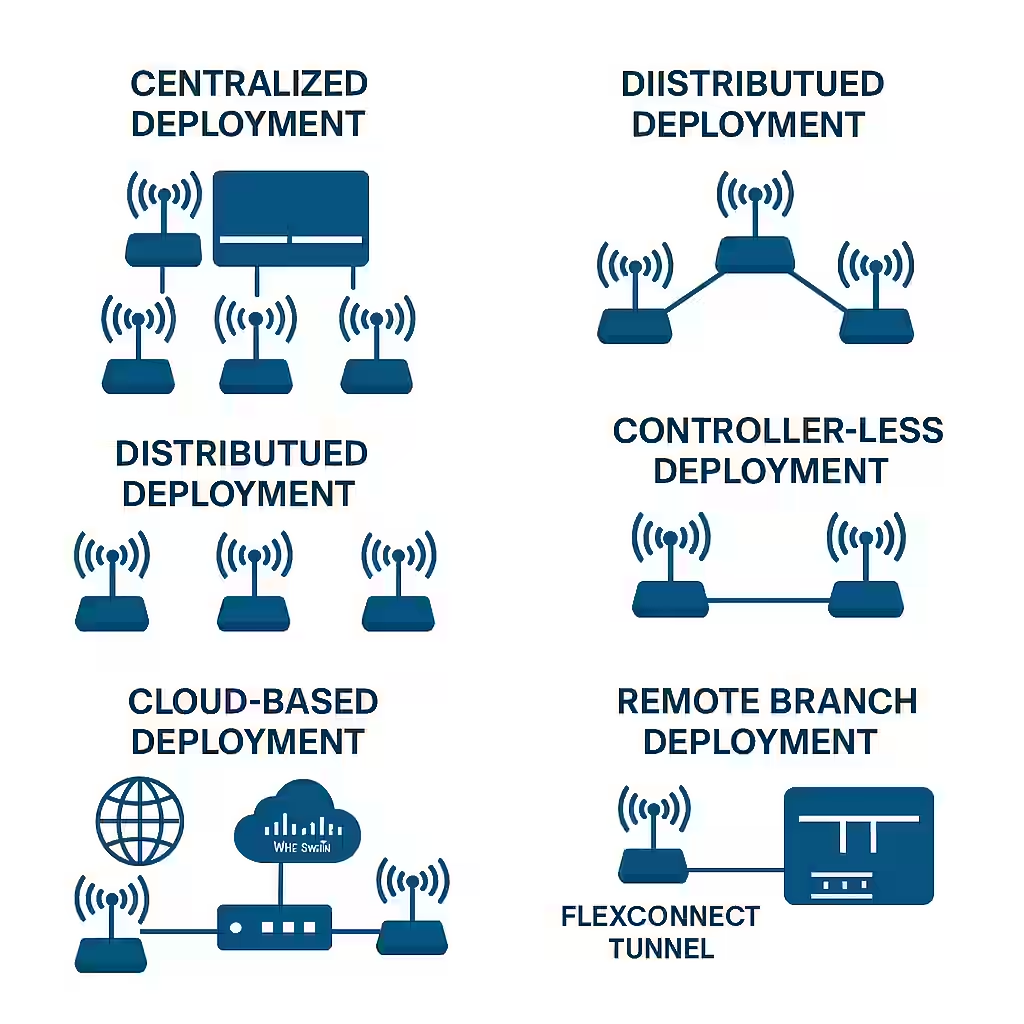
Centralized (Controller-Based) Deployment
All access points (APs) forward traffic and control functions to a central Wireless LAN Controller (WLC). The WLC manages configurations, security, and policies.
- Ideal for: Medium to large campus networks
- Benefits: Centralized management, scalability, policy consistency
- Drawback: Controller is a single point of failure without redundancy
Distributed (Autonomous) Deployment
Each AP operates independently, making its own decisions and handling management and data forwarding locally.
- Ideal for: Small offices or isolated deployments
- Benefits: Simple setup, no need for central controller
- Drawback: Difficult to manage at scale, lacks centralized control
Controller-Less (Mobility Express or Embedded WLC)
An AP takes on the role of a controller for a small group of APs, combining the benefits of centralized and autonomous deployments.
- Ideal for: Small to mid-sized businesses
- Benefits: Centralized-like management without dedicated WLC
- Drawback: Limited scalability
Cloud-Based Deployment
APs connect to a cloud-managed platform (e.g., Cisco Meraki), which handles configuration, monitoring, and updates.
- Ideal for: Multi-site businesses, retail chains
- Benefits: Easy remote management, reduced on-site IT needs
- Drawback: Requires reliable internet connectivity
Remote Branch Deployment
Designed for branch offices connected to a central hub, often using FlexConnect or SD-Branch solutions. Local switching is available even if WAN fails.
- Ideal for: Branch offices with limited IT resources
- Benefits: Central control, local resiliency
- Drawback: Complex WAN dependency if not configured properly
Considerations When Choosing a Model
- Scale: How many APs and locations are needed?
- Control: Is centralized management essential?
- Resiliency: What happens during WAN outages?
- IT Resources: Is there staff available for on-site management?
- Cost: Budget for hardware, licenses, and ongoing support
Config Insight: Basic AP Registration with Controller
AP# capwap ap controller ip address 192.168.100.10