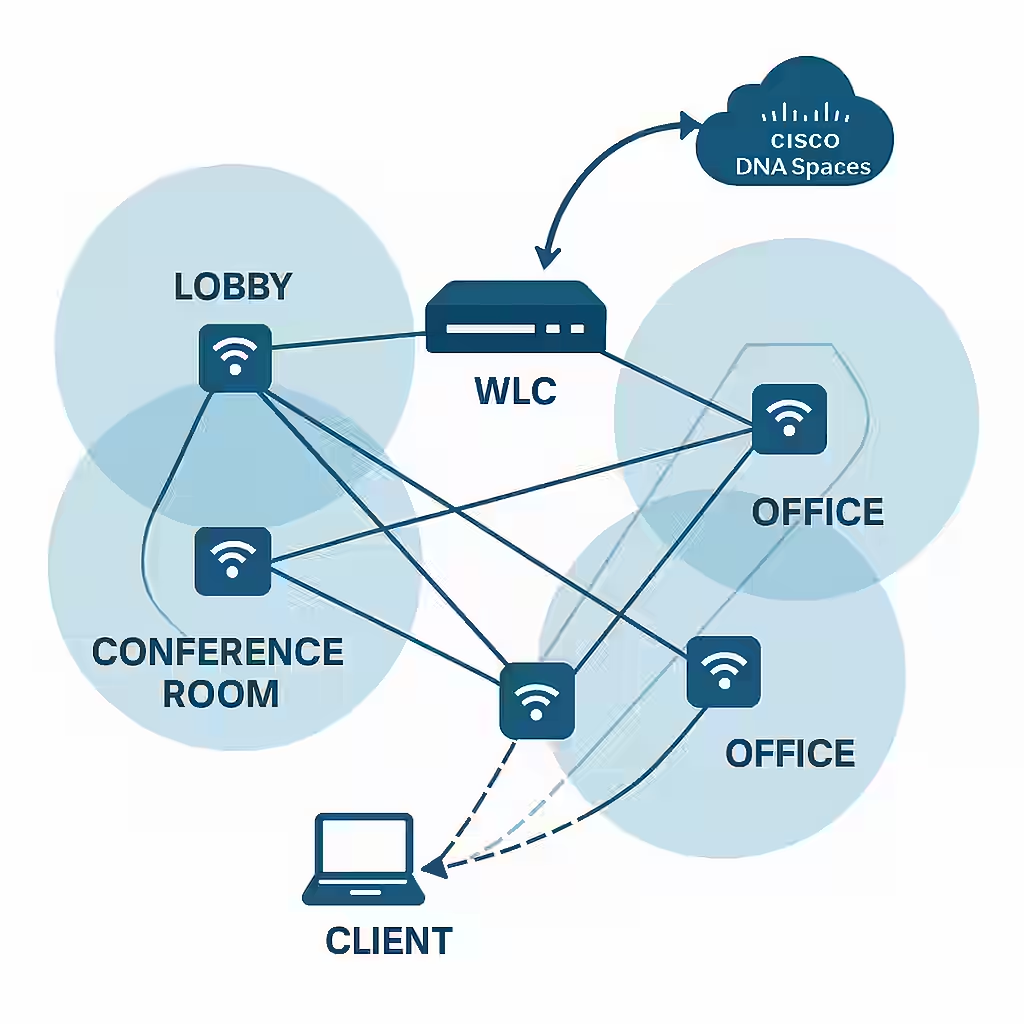
Wi-Fi is no longer just about internet access—it’s about intelligence. Modern wireless LANs (WLANs) do more than connect devices; they can track their location. Location services have become a powerful tool in environments like healthcare, retail, manufacturing, and even smart campuses, providing insights into movement, usage, and security.
Why Location Services Matter
Knowing where a device is within a building can improve safety, enhance customer experience, and streamline operations. From tracking assets in hospitals to pushing promotions in retail stores, WLAN-based location services unlock a new layer of network value.
Key Concepts
1. Types of WLAN Location Services
- Presence: Detects if a device is in the area—basic, but useful for foot traffic analysis.
- Zone-Based Location: Identifies general areas or zones where a device is located (e.g., lobby, office).
- XY Location (Real-Time Location Services or RTLS): Tracks exact coordinates within a space.
- Z-Axis (Vertical Positioning): Determines floor level in multistory buildings.
2. Technologies Behind Location Services
- RSSI (Received Signal Strength Indicator): Measures signal strength from APs to estimate proximity. Simple but affected by walls and interference.
- TDoA (Time Difference of Arrival): Measures time for signals to reach multiple APs to triangulate position. More accurate but requires tight synchronization.
- Angle of Arrival (AoA): Uses antenna arrays to calculate direction of the signal. High precision in newer deployments.
- BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy): Often used in conjunction with Wi-Fi for hyperlocal accuracy.
3. Location Engines and Platforms
- Cisco DNA Spaces: Offers presence analytics, location heat maps, behavior patterns, and integration with business applications.
- Cisco CMX (Connected Mobile Experiences): Legacy platform for location tracking and analytics.
Considerations for WLAN Location Design
- Access Point Density: Minimum of 3 APs in range for accurate triangulation.
- AP Placement: Uniform spacing and low mounting height improve precision.
- Calibration: Perform RF fingerprinting for higher accuracy, especially in RTLS.
- Device Type Awareness: Different devices report RSSI differently—consider in tuning.
- Privacy and Compliance: Implement policies that align with data protection regulations.
Config Insight: Enabling Location Services on a Cisco WLC
wlc# config location enable
wlc# config location history enableNote: Advanced location features typically require integration with Cisco DNA Spaces or CMX.